INTRODUCTION TO BUILDING INFORMATION MODELING (BIM)
The Digital Transformation of Construction
In today’s construction industry, Building Information Modeling (BIM) is no longer a buzzword — it is a necessity. Architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers now rely on BIM to design, deliver, and operate projects more efficiently through improved collaboration and information management.
What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a built asset. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM uses intelligent 3D models that integrate geometry, data, and project processes across the entire lifecycle — from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
Core Principle: BIM is not just about 3D modeling; it is about information management and collaboration.
Industry Context and Market Growth
BIM adoption continues to grow globally. Industry reports indicate that over 70% of construction professionals now use BIM workflows, and the global BIM market is projected to expand significantly in the coming years.
- Singapore is a leader in BIM implementation, with progressive BIM e-submission requirements introduced by the Building and Construction Authority (BCA).
- United Kingdom public projects transitioned from the BIM Level 2 mandate to the ISO 19650 information management framework.
- Emerging markets, including Myanmar, are increasingly adopting BIM to align with international project standards.
BIM Dimensions: Beyond 3D Visualization
The “dimensions of BIM” concept is an industry convention, used to describe how information layers are added to the model.
| Dimension | Description | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 3D – Geometric Modeling | Spatial design and visualization | Coordination, clash detection, stakeholder communication |
| 4D – Time | Construction scheduling | Sequencing, logistics planning, progress tracking |
| 5D – Cost | Quantity and cost integration | Quantity takeoff, cost planning, budget control |
| 6D – Sustainability | Environmental performance | Energy simulation, carbon analysis, lifecycle impact |
| 7D – Facility Management | Asset information | Maintenance planning, space management, operations |
Each added dimension transforms the model from a visual tool into a decision-making platform.
Benefits of BIM
Organizations that implement BIM effectively achieve:
- Reduced rework through clash detection
- Improved cost certainty
- Faster project delivery
- Better interdisciplinary collaboration
- Enhanced building performance after handover
International Standards: ISO 19650 Series
Professional BIM implementation follows internationally recognized standards to ensure consistent information management.
| Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ISO 19650-1 | Concepts and principles of BIM information management |
| ISO 19650-2 | Information management during design and construction |
| ISO 19650-3 | Information management during asset operation |
| ISO 19650-4 | Information exchange requirements |
| ISO 19650-5 | Security-minded information management |
Common Data Environment (CDE)
A Common Data Environment is a centralized platform for managing project information.
Typical Workflow States:
- Work in Progress (WIP) – Active model development
- Shared – Coordination and review
- Published – Approved for construction
- Archived – Historical record
The CDE ensures a single source of truth and prevents version conflicts.
Level of Development (LOD): Model Maturity
LOD describes the reliability and development of model elements. LOD definitions must always be project-specific and documented in the BIM Execution Plan.
| LOD | Description | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| LOD 100 | Conceptual representation | Feasibility studies, massing |
| LOD 200 | Approximate geometry | Schematic design, early costing |
| LOD 300 | Accurate design intent | Construction documents, coordination |
| LOD 350 | Interfaces and connections | Trade coordination |
| LOD 400 | Fabrication and assembly detail | Shop drawings, installation |
| LOD 500 | Field-verified representation | Facility management and operations |
LOD 500 represents verified asset information, not necessarily fabrication-level detail.
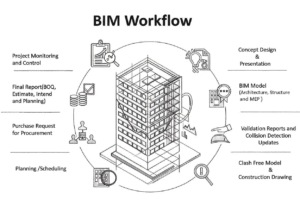
BIM Workflow Across the Project Lifecycle
- Concept design and visualization
- Multidisciplinary model development (Architecture, Structure, MEP)
- Clash detection and validation
- Coordinated model and construction documentation
- 4D planning and scheduling
- 5D quantity takeoff and cost planning
- Project information model deliverables
- Construction monitoring and control
- Asset information model and handover
Data Exchange and Interoperability
- IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) – Open standard (ISO 16739) for model exchange
- COBie – Structured asset data format for facility management handover
Common BIM Software Ecosystem
- Authoring: Revit, ArchiCAD, Tekla Structures, Bentley OpenBuildings
- Coordination: Navisworks, Solibri, BIM 360, Trimble Connect
- Analysis: IES VE, DesignBuilder, Insight, ETABS
- Facility Management: Archibus, TRIRIGA, FM:Systems
BIM Execution Plan (BEP)
A BIM project requires a structured BIM Execution Plan covering:
- Information requirements
- Standards and naming conventions
- Roles and responsibilities
- Software and data exchange
- Quality assurance procedures
Emerging Technologies Integrated with BIM
- Digital Twins – Real-time asset monitoring
- Artificial Intelligence – Automated checks and predictive analysis
- Reality Capture – Laser scanning and point-cloud modeling
- Extended Reality (XR) – VR/AR/MR for review and site use
Conclusion: The Future is Digital
BIM has fundamentally transformed construction by enabling smarter decision-making, higher quality, and improved lifecycle performance. As AI, IoT, and digital twins become mainstream, BIM serves as the foundational data environment for future smart buildings and cities.
For developing construction markets, BIM adoption represents a major opportunity to align with international standards and compete globally.